All You Need to Know About Bursitis
All You Need to Know About Bursitis
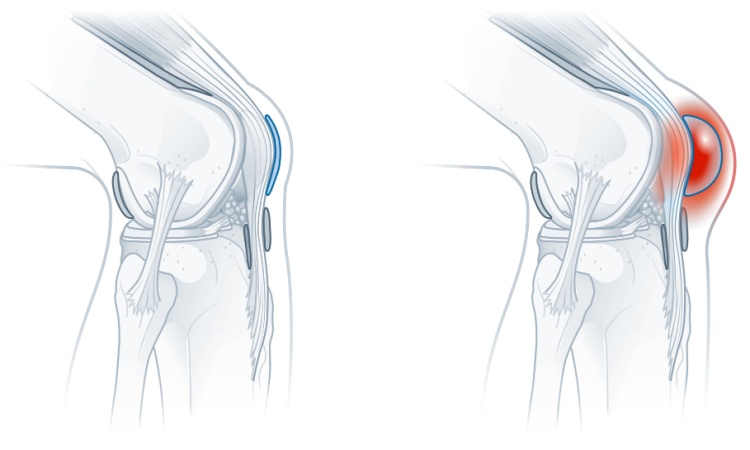
Bursitis is an inflammation of your bursae, which are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the muscles, bones, and tendons near the joints. These sacs help in the smooth movement of the joints. When bursae become inflamed, it can cause pain and discomfort in the affected joints. Bursitis commonly occurs in joints where there is frequent repetitive movement, such as the elbow, shoulders, hips, knees, and heels.
All You Need to Know About Bursitis
Now that you know what is bursitis, it is also important to know its symptoms, causes, risk factors, and how it can be treated.
Symptoms of Bursitis
Some of the common symptoms of bursitis are:
• Sharp pain in the affected joint, particularly when you move or apply pressure to it.
• Swelling around the affected area.
• Redness and warmth in the affected area.
• Stiffness in the affected joints, especially after prolonged rest or periods of inactivity.
• The joint's range of motion will be restricted, making it painful or difficult to move fully.
• Tenderness, i.e., the area will feel tender or sore when you touch it.
Causes of Bursitis
The most common cause of bursitis is overuse of the bursa. The other causes are:
• Repetitive movement:
If you are involved in activities or occupations that require repetitive movements or pressure on a specific joint, it can lead to bursitis.
• Poor posture:
Poor posture during physical activities can put stress on the joints, causing inflammation of the bursae.
• Trauma or injury:
A sudden injury or trauma to the affected area due to a fall or a direct blow.
• Prolonged pressure:
Leaning on your elbows for prolonged periods, sitting or standing in a way that puts pressure on a specific area, repeatedly bending your knees, or excessive kneeling can cause bursitis.
• Age:
With age, tendons can lose elasticity, making them vulnerable to bursitis.
• Infection:
Infections can cause bursitis, though it is rare.
• Medical conditions:
People with certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, gout, or thyroid disorders, are at a higher risk of bursitis.
• Obesity:
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of knee and hip bursitis.
Treatment for Bursitis
Bursitis usually heals on its own with rest and at-home treatments. You must avoid activities that worsen the symptoms of bursitis and give the affected area adequate rest. Applying ice packs and taking over-the-counter pain relievers can also provide relief. However, if conservative treatments fail to work, you may require:
• Antibiotics:
If an infection causes bursitis, you may be prescribed antibiotics. If the infection is very serious, you may have to take antibiotics through IV in a hospital.
• Physical therapy:
Physical therapy strengthens the muscles in the affected joint, improves range of motion, and provides relief from pain. It also prevents the recurrence of bursitis.
• Injections:
If the inflammation and pain are severe, corticosteroid injections may be recommended. It will be injected into the bursa, easing the pain and discomfort.
• Supported device:
Depending on the location of your bursitis, your doctor may recommend a splint, cane, or crutches, but for a temporary period. These devices can help reduce stress on the affected joints and promote healing.
• Surgery:
Surgical removal of the bursa is considered the last resort when other treatments are ineffective or in cases of chronic bursitis. However, this is rare.
How to Prevent Bursitis
While bursitis cannot always be prevented, you can reduce the risk with some basic lifestyle modifications. Here are some tips:
• Maintain a healthy weight:
If you are overweight, your joints, especially your hips and knees, will be under more pressure, increasing the risk of bursitis. Ensure you maintain a healthy weight with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
• Strengthen your muscles:
Regular exercise can strengthen your muscles around the joints, reducing stress on the joints and protecting the affected joint.
• Take breaks:
Make sure you take regular breaks if your work involves repetitive joint movements.
• Warm up:
Before starting any exercises or strenuous activities, ensure you warm up and stretch. This will help prevent injury.
• Maintain good posture:
Whether you are sitting, standing, working, or exercising, it is important to maintain good posture as this will help prevent any stress on the joints.
• Protective equipment:
If you are kneeling or sitting on a hard surface because your work demands it, it is advisable to use knee pads or cushions to reduce the pressure on joints.
Conclusion
Bursitis usually gets better on its own by giving rest to the affected joints and with home remedies. However, if the pain persists, interfering with your day-to-day activities, and if the soreness, swelling, or redness in the affected area doesn't improve with home treatments, you must seek medical attention.
A health insurance policy will be of immense financial support during medical emergencies, as it will cover treatment costs and reduce out-of-pocket expenses.
Disclaimer: The above information is for illustrative purposes only. For more details, please refer to the policy wordings and prospectus before concluding the sales.
RELATED ARTICLES
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Beyond Joint Pain - The Hidden Effects on Overall Health
How is Osteoarthritis Detected?
Arthritis Myths vs Facts: Things You Need To Know










 Health Insurance
Health Insurance  Travel Insurance
Travel Insurance  Car Insurance
Car Insurance  Cyber Insurance
Cyber Insurance  Critical Illness Insurance
Critical Illness Insurance
 Pet Insurance
Pet Insurance
 Bike/Two Wheeler Insurance
Bike/Two Wheeler Insurance  Home Insurance
Home Insurance  Third Party Vehicle Ins.
Third Party Vehicle Ins.  Tractor Insurance
Tractor Insurance  Goods Carrying Vehicle Ins.
Goods Carrying Vehicle Ins.  Passenger Carrying Vehicle Ins.
Passenger Carrying Vehicle Ins.  Compulsory Personal Accident Insurance
Compulsory Personal Accident Insurance  Travel Insurance
Travel Insurance  Rural
Rural 











