

What to Eat for Healthier Aging? Here's How Your Nutritional Needs Change as You Age
With the increase in age, you have to be more concerned about your health as numerous changes occur in the body. With aging, the body's muscle mass starts to drop, the skin gets thinner, and appetite also reduces. The two most important things to delay your aging are checking your nutritional needs as you grow older and stay active. Whether you are old or young, ensure that you follow a healthier lifestyle to incorporate exercise and a healthy diet in your daily routine. Adequate hours of sleep is also necessary to look younger as you age.
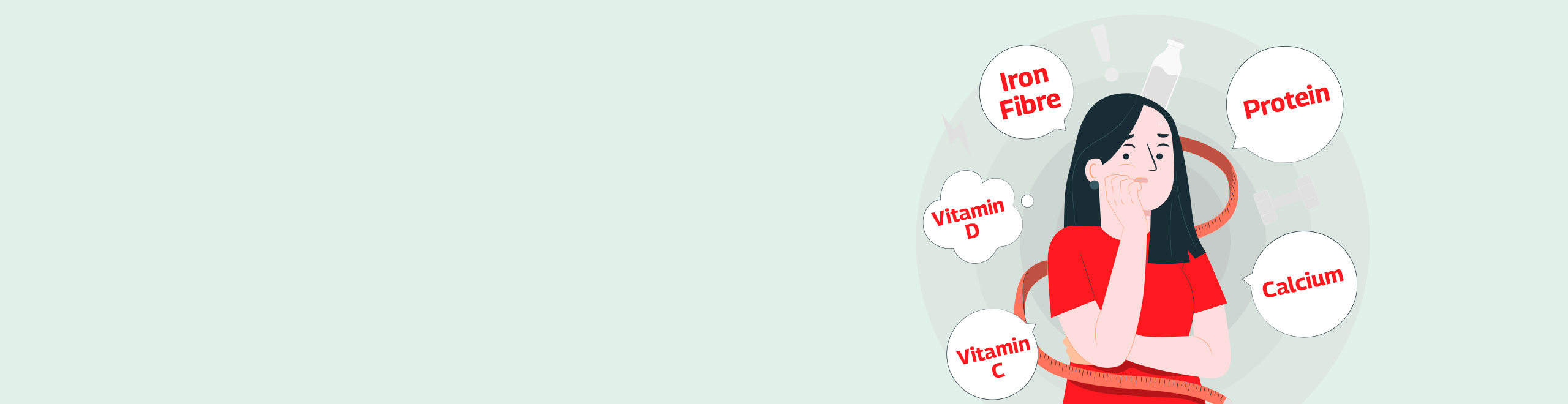
When it comes to nutritional needs, it has to be changed when your body starts aging. The most important reason is nutritional deficiencies in older people. When the body grows older, it produces less stomach acid, affecting the absorption of micronutrients, such as vitamin B12, calcium, iron, and magnesium. With the increase in age, calorie intake also reduces, which creates a nutritional dilemma. Older adults need to get the Recommended Dietary Intake (RDI) of all nutrients from fewer calories. When the person starts to age, the body's ability to recognize vital senses like hunger and thirst also reduces, leading to unintentional weight loss and dehydration.
Needing Fewer Calories, but More Nutrients
With the increase in age, the body's daily calorie requirement reduces due to a reduction in basal metabolic rate (BMR) and muscle mass. If older adults eat the same way as they were young, they might gain fat and become overweight due to a decrease in BMR and muscle mass. High BMR and a good muscle percentage in the body help burn calories. From fewer calories, it is advisable for older adults to focus on meeting the daily requirement of the following nutrient:
1. Protein:
As per the National Institute of Health study, an average adult loses 3 to 8% of their muscle mass each decade after age 30. The condition where the body starts to lose muscle mass and strength is known as sarcopenia, a major cause of weakness, fractures, and poor health. Therefore, eating a good amount of protein daily can help the body maintain muscle and fight sarcopenia. Also, if a protein-rich diet is combined with weight training exercises, it can effectively help fight sarcopenia.
2. Calcium:
Aging leads to hormonal changes in the body, which might decrease calcium absorption as it increases the loss of this micronutrient through the kidneys. Apart from this, when the body starts to age, you may become lactose intolerant, where the body loses the ability to digest sugar. Due to this condition, some people decrease their intake of dairy products, which are good sources of calcium. However, the body needs to get the required amount of calcium daily and if the body gets lactose intolerant, then this micronutrient can be sourced from veggies or supplementation
3. Iron:
This nutrient deficiency is quite common in older people, which may cause anemia, where the blood does not supply enough oxygen to the body. Iron can be sourced from red meats, poultry, fish, lentils, spinach, beet, to name a few.
4. Vitamin C:
Vitamin C helps absorb more iron from foods; ensure that you include iron foods with vitamin C rich ingredients in the same meal. For example, squeeze lemon on spinach while having it; it will help the body absorb more iron. Apart from this, vitamin C also strengthens immunity and increases collagen production, which improves skin and hair growth.
5. Vitamin D:
Reduction in calcium absorption is caused due to vitamin D deficiency. This leads to bones weakening, which might increase the risk of fractures. Vitamin D can be sourced from a variety of fish, such as salmon and herring.
6. Fibre:
Older adults tend to move less and are likely to take medications that can have constipation as a side effect. A high fibre diet help relieve constipation as this nutrient passes through the gut undigested, which help form stool and promote regular bowel movements.
7. Potassium:
As you age, it is advisable to increase potassium, which helps lower the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease and kidney stones which are more common among the elderly.
Conclusion
Apart from checking the nutritional needs as per your age, managing stress for good health is also necessary. From a nutritional perspective, it is advisable for older adults to have less energy-dense fast foods and have more energy-diluted grains, vegetables and fruits. For healthier aging, a person must also stay happy, take out time for meditation, exercise or outdoor activities like walking, swimming and cycling.
Disclaimer: This blog provides general information and discussions about health and related subjects. The information and other content provided in this blog, website or in any linked materials are not intended and should not be considered, or used as a substitute for, medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Kindly contact your Doctor before starting a new medicine or health regime.
Related Articles
Nutrition Matters - Eat Healthy To Maintain Fitness!
New Diet Trends You Need To Watch Out For In 2022
How To Start A Diet And Sustain It?
Published on December 17, 2021













 Health Insurance
Health Insurance  Travel Insurance
Travel Insurance  Car Insurance
Car Insurance  Cyber Insurance
Cyber Insurance  Critical Illness Insurance
Critical Illness Insurance
 Pet Insurance
Pet Insurance
 Bike/Two Wheeler Insurance
Bike/Two Wheeler Insurance  Home Insurance
Home Insurance  Third Party Vehicle Ins.
Third Party Vehicle Ins.  Tractor Insurance
Tractor Insurance  Goods Carrying Vehicle Ins.
Goods Carrying Vehicle Ins.  Passenger Carrying Vehicle Ins.
Passenger Carrying Vehicle Ins.  Compulsory Personal Accident Insurance
Compulsory Personal Accident Insurance  Travel Insurance
Travel Insurance  Rural
Rural